查询参数和字符串验证¶
FastAPI 允许您为参数声明额外的信息和验证。
让我们以这个应用程序为例
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
查询参数 q 的类型为 str | None,这意味着它是一个 str 类型,但也可以是 None,事实上,默认值为 None,所以 FastAPI 会知道它不是必需的。
注意
由于默认值 = None,FastAPI 会知道 q 的值不是必需的。
拥有 str | None 将使您的编辑器为您提供更好的支持并检测错误。
附加验证¶
我们将强制要求,即使 q 是可选的,但只要提供了它,其长度不超过 50 个字符。
导入 Query 和 Annotated¶
为了实现这一点,首先导入
- 来自
fastapi的Query - 来自
typing的Annotated
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str | None, Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
信息
FastAPI 在 0.95.0 版本中添加了对 Annotated 的支持(并开始推荐它)。
如果您的版本较旧,尝试使用 Annotated 时会出错。
请确保您将 FastAPI 版本升级 到至少 0.95.1 后再使用 Annotated。
在 q 参数的类型中使用 Annotated¶
还记得我之前告诉过您 Annotated 可用于在 Python 类型简介 中为您的参数添加元数据吗?
现在是时候将其与 FastAPI 一起使用了。 🚀
我们有了这个类型注解
q: str | None = None
q: Union[str, None] = None
我们将使用 Annotated 来包装它,因此它变成了
q: Annotated[str | None] = None
q: Annotated[Union[str, None]] = None
这两个版本的意思相同,q 是一个可以是 str 或 None 的参数,并且默认情况下它是 None。
现在让我们来点有趣的。 🎉
在 q 参数的 Annotated 中添加 Query¶
现在我们有了这个 Annotated,可以在其中放入更多信息(在本例中为附加验证),在 Annotated 中添加 Query,并将 max_length 参数设置为 50
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str | None, Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
请注意,默认值仍然是 None,因此该参数仍然是可选的。
但是现在,在 Annotated 中拥有 Query(max_length=50),我们是在告诉 FastAPI 我们希望为该值进行附加验证,我们希望它最多包含 50 个字符。 😎
提示
这里我们使用 Query() 因为这是一个查询参数。稍后我们将看到其他参数,如 Path()、Body()、Header() 和 Cookie(),它们也接受与 Query() 相同的参数。
FastAPI 现在将
- 验证数据,确保最大长度为 50 个字符
- 当数据无效时,向客户端显示清晰的错误
- 记录 OpenAPI 架构路径操作中的参数(因此它将显示在自动文档 UI 中)
替代(旧):将 Query 作为默认值¶
FastAPI 的早期版本(0.95.0 之前)要求您将 Query 用作参数的默认值,而不是将其放在 Annotated 中,您很有可能会看到使用它的代码,因此我将向您解释。
提示
对于新代码以及尽可能使用 Annotated,如上所述。有许多优点(如下所述),没有缺点。 🍰
这就是您如何将 Query() 用作函数参数的默认值,并将 max_length 参数设置为 50
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str | None, Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(max_length=50)] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
在此情况下(不使用 Annotated),我们需要将函数中的默认值 None 替换为 Query(),我们现在需要使用 Query(default=None) 参数设置默认值,它具有定义默认值的相同目的(至少对 FastAPI 而言)。
所以
q: str | None = Query(default=None)
...使参数成为可选的,默认值为 None,与
q: str | None = None
但 Query 版本明确将其声明为查询参数。
然后,我们可以将更多参数传递给 Query。在这种情况下,max_length 参数适用于字符串
q: str | None = Query(default=None, max_length=50)
这将验证数据,在数据无效时显示清晰的错误,并记录路径操作的 OpenAPI 架构中的参数。
将 Query 作为默认值或在 Annotated 中使用¶
请记住,当在 Annotated 中使用 Query 时,不能为 Query 使用 default 参数。
相反,使用函数参数的实际默认值。否则,它将不一致。
例如,这是不允许的
q: Annotated[str, Query(default="rick")] = "morty"
...因为不清楚默认值应该是 "rick" 还是 "morty"。
所以,您将使用(最好)
q: Annotated[str, Query()] = "rick"
...或者在旧代码库中,您会发现
q: str = Query(default="rick")
Annotated 的优点¶
推荐使用 Annotated 而不是函数参数中的默认值,它在多方面都更好。 🤓
函数参数的默认值是实际的默认值,这与 Python 总体上更直观。 😌
您可以在其他地方调用同一个函数而不使用 FastAPI,它将如预期工作。如果有一个必需的参数(没有默认值),您的编辑器会通过错误提示您,如果您在不传递必需参数的情况下运行它,Python 也会报错。
当您不使用 Annotated 而使用(旧)默认值样式时,如果您在其他地方不使用 FastAPI 调用该函数,您必须记住为函数传递参数才能使其正常工作,否则值将与您期望的不同(例如,QueryInfo 或类似的东西而不是 str)。您的编辑器不会报错,Python 在运行该函数时也不会报错,只有当内部操作出错时才会。
因为 Annotated 可以有多个元数据注解,您现在甚至可以使用相同的函数与其他工具(如 Typer)配合使用。 🚀
添加更多验证¶
您还可以添加 min_length 参数
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[str | None, Query(min_length=3, max_length=50)] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(min_length=3, max_length=50)] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = Query(default=None, min_length=3, max_length=50)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, min_length=3, max_length=50),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
添加正则表达式¶
您可以定义一个 正则表达式 pattern,参数应匹配
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
str | None, Query(min_length=3, max_length=50, pattern="^fixedquery$")
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
Union[str, None], Query(min_length=3, max_length=50, pattern="^fixedquery$")
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: str | None = Query(
default=None, min_length=3, max_length=50, pattern="^fixedquery$"
),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Union[str, None] = Query(
default=None, min_length=3, max_length=50, pattern="^fixedquery$"
),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
这个特定的正则表达式模式检查接收到的参数值
^:以以下字符开头,前面没有字符。fixedquery:具有确切的值fixedquery。$:在此结束,fixedquery之后没有其他字符。
如果您对所有这些“正则表达式”想法感到迷茫,请不要担心。它们对许多人来说是一个很难的话题。您仍然可以完成很多事情而无需使用正则表达式。
现在您知道,每当您需要它们时,您都可以在FastAPI 中使用它们。
默认值¶
您当然可以使用除 None 之外的默认值。
假设您想声明 q 查询参数的 min_length 为 3,并且默认值为 "fixedquery"
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str, Query(min_length=3)] = "fixedquery"):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str = Query(default="fixedquery", min_length=3)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
注意
拥有任何类型的默认值,包括 None,都会使参数成为可选的(非必需的)。
必需参数¶
当我们不需要声明更多验证或元数据时,可以通过不声明默认值来使 q 查询参数成为必需的,例如
q: str
而不是
q: str | None = None
但是我们现在正在使用 Query 声明它,例如
q: Annotated[str | None, Query(min_length=3)] = None
因此,当您需要使用 Query 声明一个值作为必需时,您可以简单地不声明默认值
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str, Query(min_length=3)]):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str = Query(min_length=3)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
必需,可为 None¶
您可以声明一个参数可以接受 None,但它仍然是必需的。这将迫使客户端发送一个值,即使该值是 None。
为此,您可以声明 None 是一个有效类型,但只需不声明默认值
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str | None, Query(min_length=3)]):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(min_length=3)]):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = Query(min_length=3)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(min_length=3)):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
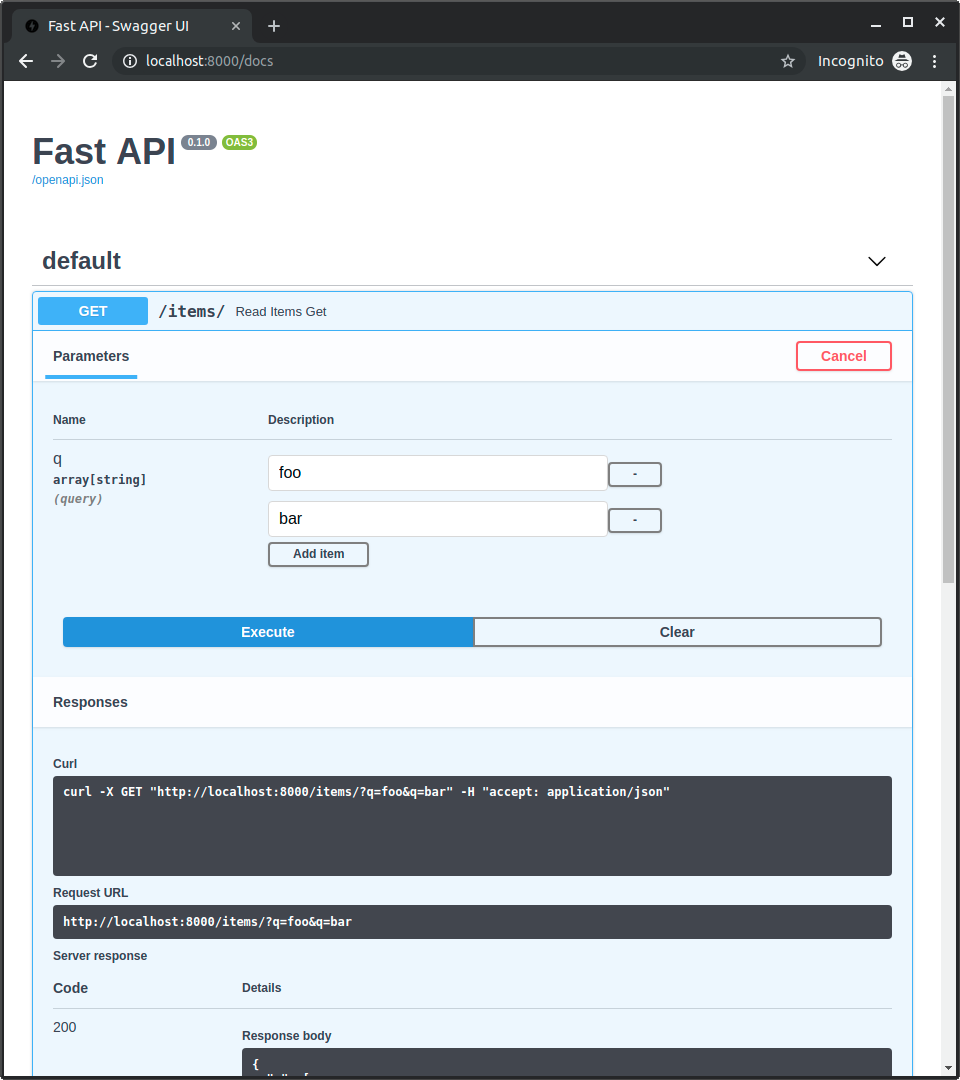
查询参数列表 / 多个值¶
当您使用 Query 显式定义查询参数时,您还可以声明它接收一个值列表,或者换句话说,接收多个值。
例如,要声明一个可以多次出现在 URL 中的查询参数 q,您可以编写
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[list[str] | None, Query()] = None):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[list[str], None], Query()] = None):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: list[str] | None = Query(default=None)):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[list[str], None] = Query(default=None)):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
然后,使用类似这样的 URL
https://:8000/items/?q=foo&q=bar
您将在路径操作函数的函数参数 q 中收到多个 q 查询参数的值(foo 和 bar),它们都在一个 Python list 中。
因此,对该 URL 的响应将是
{
"q": [
"foo",
"bar"
]
}
提示
要声明类型为 list 的查询参数,如上面的示例所示,您需要显式使用 Query,否则它将被解释为请求正文。
交互式 API 文档将相应更新,以允许多个值
查询参数列表 / 多个值及默认值¶
如果没有提供值,您也可以定义一个默认的 list 值
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[list[str], Query()] = ["foo", "bar"]):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
🤓 其他版本和变体
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: list[str] = Query(default=["foo", "bar"])):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
如果您访问
https://:8000/items/
q 的默认值将是:["foo", "bar"],您的响应将是
{
"q": [
"foo",
"bar"
]
}
仅使用 list¶
您也可以直接使用 list 而不是 list[str]
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[list, Query()] = []):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
🤓 其他版本和变体
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: list = Query(default=[])):
query_items = {"q": q}
return query_items
注意
请记住,在这种情况下,FastAPI 不会检查列表的内容。
例如,list[int] 将检查(并记录)列表的内容是整数。但仅使用 list 则不会。
声明更多元数据¶
您可以添加有关参数的更多信息。
该信息将包含在生成的 OpenAPI 中,并由文档用户界面和外部工具使用。
注意
请记住,不同的工具可能具有不同级别的 OpenAPI 支持。
其中一些可能尚未显示所有声明的额外信息,尽管在大多数情况下,缺失的功能已计划开发。
您可以添加一个 title
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[str | None, Query(title="Query string", min_length=3)] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(title="Query string", min_length=3)] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: str | None = Query(default=None, title="Query string", min_length=3),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, title="Query string", min_length=3),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
和一个 description
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
str | None,
Query(
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
),
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
Union[str, None],
Query(
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
),
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: str | None = Query(
default=None,
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Union[str, None] = Query(
default=None,
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
别名参数¶
假设您希望参数为 item-query。
就像在
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?item-query=foobaritems
但 item-query 不是有效的 Python 变量名。
最接近的是 item_query。
但您仍然需要它完全是 item-query...
然后您可以声明一个 alias,该别名将用于查找参数值
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[str | None, Query(alias="item-query")] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(alias="item-query")] = None):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = Query(default=None, alias="item-query")):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, alias="item-query")):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
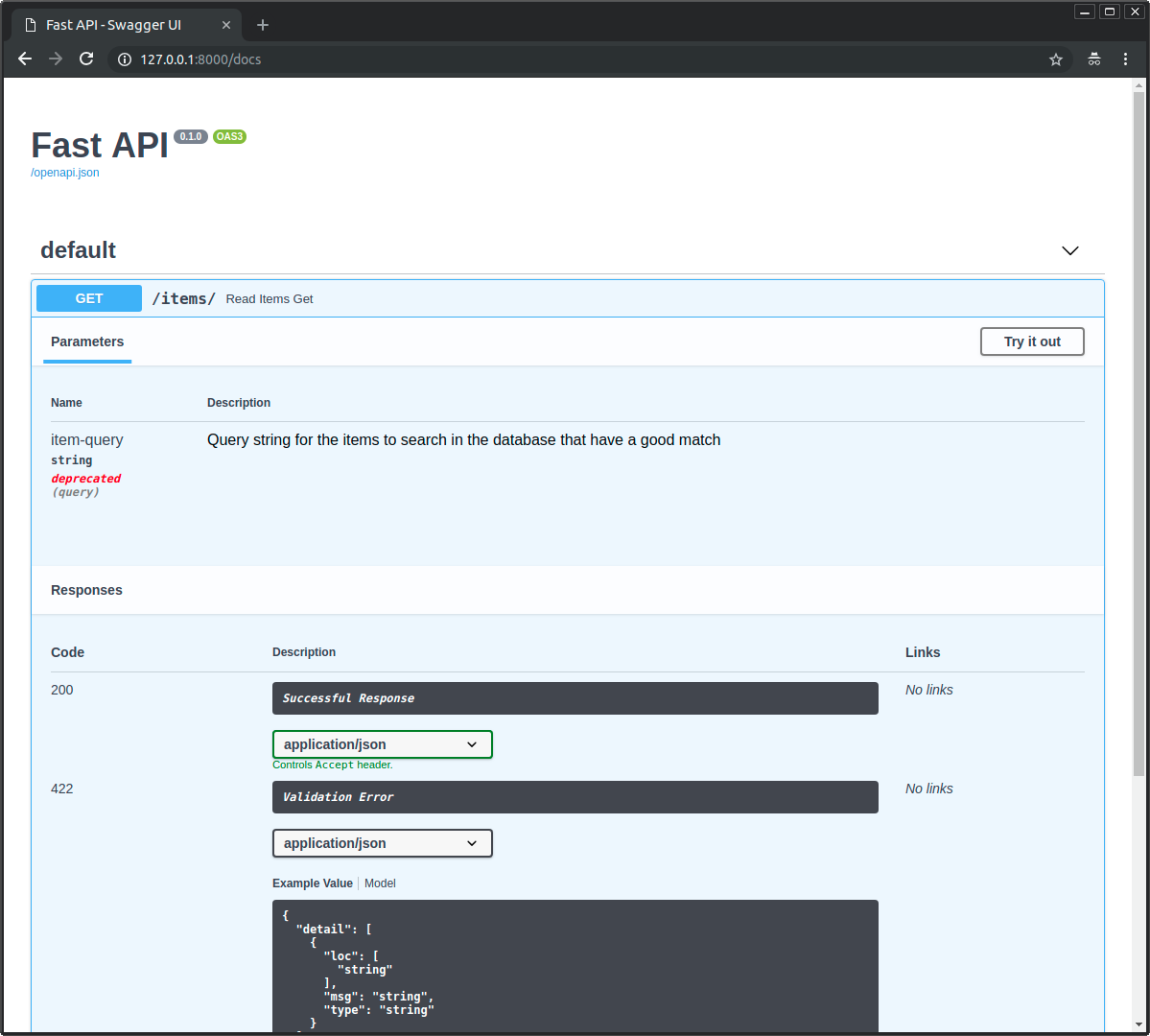
弃用参数¶
现在假设您不再喜欢这个参数。
您必须暂时将其保留,因为有客户端正在使用它,但您希望文档清楚地将其显示为已弃用。
然后将 deprecated=True 参数传递给 Query
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
str | None,
Query(
alias="item-query",
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
max_length=50,
pattern="^fixedquery$",
deprecated=True,
),
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Annotated[
Union[str, None],
Query(
alias="item-query",
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
max_length=50,
pattern="^fixedquery$",
deprecated=True,
),
] = None,
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: str | None = Query(
default=None,
alias="item-query",
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
max_length=50,
pattern="^fixedquery$",
deprecated=True,
),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
q: Union[str, None] = Query(
default=None,
alias="item-query",
title="Query string",
description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",
min_length=3,
max_length=50,
pattern="^fixedquery$",
deprecated=True,
),
):
results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}
if q:
results.update({"q": q})
return results
文档将这样显示
从 OpenAPI 中排除参数¶
要将查询参数从生成的 OpenAPI 架构中排除(从而从自动文档系统中排除),请将 Query 的 include_in_schema 参数设置为 False
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
hidden_query: Annotated[str | None, Query(include_in_schema=False)] = None,
):
if hidden_query:
return {"hidden_query": hidden_query}
else:
return {"hidden_query": "Not found"}
🤓 其他版本和变体
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
hidden_query: Annotated[Union[str, None], Query(include_in_schema=False)] = None,
):
if hidden_query:
return {"hidden_query": hidden_query}
else:
return {"hidden_query": "Not found"}
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
hidden_query: str | None = Query(default=None, include_in_schema=False),
):
if hidden_query:
return {"hidden_query": hidden_query}
else:
return {"hidden_query": "Not found"}
提示
如果可能,请优先使用 Annotated 版本。
from typing import Union
from fastapi import FastAPI, Query
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
hidden_query: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, include_in_schema=False),
):
if hidden_query:
return {"hidden_query": hidden_query}
else:
return {"hidden_query": "Not found"}
自定义验证¶
在某些情况下,您需要进行自定义验证,而这些验证无法通过上面显示的参数完成。
在那些情况下,您可以使用一个自定义验证器函数,它在正常验证之后应用(例如,在验证值是 str 之后)。
您可以通过在 Annotated 中使用 Pydantic 的 AfterValidator 来实现这一点。
提示
Pydantic 还提供了 BeforeValidator 和其他函数。 🤓
例如,此自定义验证器检查项 ID 是否以 isbn- 开头(对于 ISBN 图书编号)或以 imdb- 开头(对于 IMDB 电影 URL ID)
import random
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import AfterValidator
app = FastAPI()
data = {
"isbn-9781529046137": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"imdb-tt0371724": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"isbn-9781439512982": "Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 2",
}
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[str | None, AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
🤓 其他版本和变体
import random
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import AfterValidator
app = FastAPI()
data = {
"isbn-9781529046137": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"imdb-tt0371724": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"isbn-9781439512982": "Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 2",
}
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[Union[str, None], AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
信息
这在 Pydantic 版本 2 或更高版本中可用。 😎
提示
如果您需要进行任何需要与外部组件(如数据库或其他 API)进行通信的验证,您应该改用FastAPI 依赖项,稍后您将学到它们。
这些自定义验证器适用于仅使用请求中提供的相同数据即可检查的内容。
理解代码¶
关键点只是在Annotated 中使用带有函数的 AfterValidator。可以随意跳过此部分。 🤸
但是,如果您对这个特定的代码示例感到好奇并且仍然感兴趣,这里有一些额外的细节。
使用 value.startswith() 的字符串¶
您注意到了吗?使用 value.startswith() 的字符串可以接受一个元组,它将检查元组中的每个值
# Code above omitted 👆
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
# Code below omitted 👇
👀 完整文件预览
import random
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import AfterValidator
app = FastAPI()
data = {
"isbn-9781529046137": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"imdb-tt0371724": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"isbn-9781439512982": "Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 2",
}
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[str | None, AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
🤓 其他版本和变体
import random
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import AfterValidator
app = FastAPI()
data = {
"isbn-9781529046137": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"imdb-tt0371724": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"isbn-9781439512982": "Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 2",
}
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[Union[str, None], AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
随机项¶
使用 data.items(),我们得到一个 可迭代对象,其中包含每个字典项的键和值元组。
我们使用 list(data.items()) 将此可迭代对象转换为一个真正的 list。
然后使用 random.choice(),我们可以从列表中获取一个随机值,因此,我们将获得一个包含 (id, name) 的元组。它将是类似 ("imdb-tt0371724", "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy") 的内容。
然后我们将元组的这两个值分配给变量 id 和 name。
因此,如果用户未提供项 ID,他们仍将收到一个随机建议。
...我们在一个简单的行中完成了所有这些。 🤯 您不爱 Python 吗? 🐍
# Code above omitted 👆
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[str | None, AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
👀 完整文件预览
import random
from typing import Annotated
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import AfterValidator
app = FastAPI()
data = {
"isbn-9781529046137": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"imdb-tt0371724": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"isbn-9781439512982": "Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 2",
}
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[str | None, AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
🤓 其他版本和变体
import random
from typing import Annotated, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import AfterValidator
app = FastAPI()
data = {
"isbn-9781529046137": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"imdb-tt0371724": "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy",
"isbn-9781439512982": "Isaac Asimov: The Complete Stories, Vol. 2",
}
def check_valid_id(id: str):
if not id.startswith(("isbn-", "imdb-")):
raise ValueError('Invalid ID format, it must start with "isbn-" or "imdb-"')
return id
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(
id: Annotated[Union[str, None], AfterValidator(check_valid_id)] = None,
):
if id:
item = data.get(id)
else:
id, item = random.choice(list(data.items()))
return {"id": id, "name": item}
总结¶
您可以为您的参数声明额外的验证和元数据。
通用验证和元数据
别名titledescriptiondeprecated
特定于字符串的验证
最小长度最大长度模式
使用 AfterValidator 进行自定义验证。
在这些示例中,您看到了如何为 str 值声明验证。
请参阅下一章,了解如何为其他类型(如数字)声明验证。