路径操作高级配置¶
OpenAPI operationId¶
警告
如果您不是 OpenAPI 的“专家”,您可能不需要此功能。
您可以使用参数 operation_id 设置要在您的路径操作中使用的 OpenAPI operationId。
您需要确保它对每个操作都是唯一的。
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", operation_id="some_specific_id_you_define")
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
使用路径操作函数名称作为 operationId¶
如果您想将 API 的函数名称用作 operationId,您可以遍历所有函数并使用它们的 APIRoute.name 覆盖每个路径操作的 operation_id。
您应该在添加所有路径操作后执行此操作。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from fastapi.routing import APIRoute
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
def use_route_names_as_operation_ids(app: FastAPI) -> None:
"""
Simplify operation IDs so that generated API clients have simpler function
names.
Should be called only after all routes have been added.
"""
for route in app.routes:
if isinstance(route, APIRoute):
route.operation_id = route.name # in this case, 'read_items'
use_route_names_as_operation_ids(app)
提示
如果您手动调用 app.openapi(),则应在此之前更新 operationId。
警告
如果您这样做,则必须确保每个路径操作函数都具有唯一的名称。
即使它们在不同的模块(Python 文件)中。
从 OpenAPI 中排除¶
要从生成的 OpenAPI 模式(以及自动文档系统)中排除路径操作,请使用参数 include_in_schema 并将其设置为 False
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", include_in_schema=False)
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "Foo"}]
来自文档字符串的高级描述¶
您可以限制从路径操作函数的文档字符串中用于 OpenAPI 的行数。
添加 \f(一个转义的“换页符”字符)会导致 FastAPI 在此点截断用于 OpenAPI 的输出。
它不会显示在文档中,但其他工具(如 Sphinx)将能够使用其余部分。
from typing import Set, Union
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
description: Union[str, None] = None
price: float
tax: Union[float, None] = None
tags: Set[str] = set()
@app.post("/items/", response_model=Item, summary="Create an item")
async def create_item(item: Item):
"""
Create an item with all the information:
- **name**: each item must have a name
- **description**: a long description
- **price**: required
- **tax**: if the item doesn't have tax, you can omit this
- **tags**: a set of unique tag strings for this item
\f
:param item: User input.
"""
return item
其他响应¶
您可能已经了解了如何为路径操作声明 response_model 和 status_code。
这定义了有关路径操作主要响应的元数据。
您还可以声明其他响应及其模型、状态代码等。
文档中有一整章对此进行了介绍,您可以在 OpenAPI 中的其他响应 中阅读。
OpenAPI 额外¶
当您在应用程序中声明路径操作时,FastAPI 会自动生成有关该路径操作的相关元数据,以包含在 OpenAPI 模式中。
“技术细节”
在 OpenAPI 规范中,它被称为 操作对象。
它包含有关路径操作的所有信息,并用于生成自动文档。
它包括 tags、parameters、requestBody、responses 等。
此特定于路径操作的 OpenAPI 模式通常由 FastAPI 自动生成,但您也可以扩展它。
您可以使用参数openapi_extra扩展路径操作的OpenAPI模式。
OpenAPI 扩展¶
例如,此openapi_extra可用于声明OpenAPI 扩展
from fastapi import FastAPI
app = FastAPI()
@app.get("/items/", openapi_extra={"x-aperture-labs-portal": "blue"})
async def read_items():
return [{"item_id": "portal-gun"}]
如果您打开自动API文档,您的扩展将显示在特定路径操作的底部。
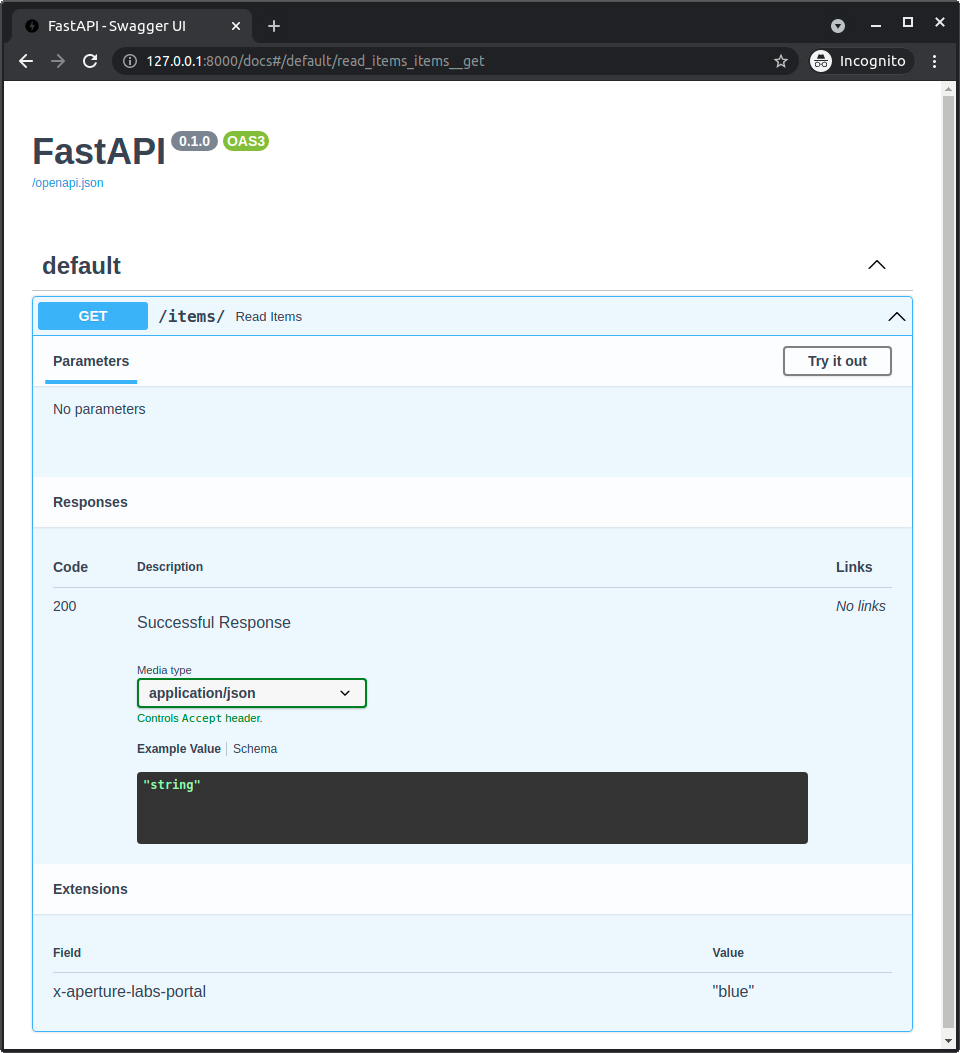
并且,如果您查看生成的OpenAPI(位于API中的/openapi.json),您也会在特定的路径操作中看到您的扩展。
{
"openapi": "3.1.0",
"info": {
"title": "FastAPI",
"version": "0.1.0"
},
"paths": {
"/items/": {
"get": {
"summary": "Read Items",
"operationId": "read_items_items__get",
"responses": {
"200": {
"description": "Successful Response",
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {}
}
}
}
},
"x-aperture-labs-portal": "blue"
}
}
}
}
自定义OpenAPI路径操作模式¶
openapi_extra中的字典将与为路径操作自动生成的OpenAPI模式深度合并。
因此,您可以向自动生成的模式添加其他数据。
例如,您可以决定使用自己的代码读取和验证请求,而不使用FastAPI与Pydantic的自动功能,但您可能仍然希望在OpenAPI模式中定义请求。
您可以使用openapi_extra来实现。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
app = FastAPI()
def magic_data_reader(raw_body: bytes):
return {
"size": len(raw_body),
"content": {
"name": "Maaaagic",
"price": 42,
"description": "Just kiddin', no magic here. ✨",
},
}
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {
"application/json": {
"schema": {
"required": ["name", "price"],
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"name": {"type": "string"},
"price": {"type": "number"},
"description": {"type": "string"},
},
}
}
},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
data = magic_data_reader(raw_body)
return data
在本例中,我们没有声明任何Pydantic模型。事实上,请求体甚至没有解析为JSON,它直接读取为bytes,并且函数magic_data_reader()将负责以某种方式解析它。
尽管如此,我们仍然可以声明请求体的预期模式。
自定义OpenAPI内容类型¶
使用相同的技巧,您可以使用Pydantic模型定义JSON模式,然后将其包含在路径操作的自定义OpenAPI模式部分中。
即使请求中的数据类型不是JSON,您也可以这样做。
例如,在此应用程序中,我们不使用FastAPI集成的功能从Pydantic模型中提取JSON模式,也不使用JSON的自动验证。事实上,我们将请求内容类型声明为YAML,而不是JSON。
from typing import List
import yaml
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
tags: List[str]
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {"application/x-yaml": {"schema": Item.model_json_schema()}},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
try:
data = yaml.safe_load(raw_body)
except yaml.YAMLError:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail="Invalid YAML")
try:
item = Item.model_validate(data)
except ValidationError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail=e.errors(include_url=False))
return item
from typing import List
import yaml
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
tags: List[str]
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {"application/x-yaml": {"schema": Item.schema()}},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
try:
data = yaml.safe_load(raw_body)
except yaml.YAMLError:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail="Invalid YAML")
try:
item = Item.parse_obj(data)
except ValidationError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail=e.errors())
return item
信息
在Pydantic版本1中,获取模型的JSON模式的方法称为Item.schema(),在Pydantic版本2中,该方法称为Item.model_json_schema()。
尽管如此,即使我们没有使用默认的集成功能,我们仍然使用Pydantic模型手动生成我们希望以YAML接收的数据的JSON模式。
然后我们直接使用请求,并将主体提取为bytes。这意味着FastAPI甚至不会尝试将请求有效负载解析为JSON。
然后在我们的代码中,我们直接解析YAML内容,然后我们再次使用相同的Pydantic模型来验证YAML内容。
from typing import List
import yaml
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
tags: List[str]
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {"application/x-yaml": {"schema": Item.model_json_schema()}},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
try:
data = yaml.safe_load(raw_body)
except yaml.YAMLError:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail="Invalid YAML")
try:
item = Item.model_validate(data)
except ValidationError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail=e.errors(include_url=False))
return item
from typing import List
import yaml
from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, Request
from pydantic import BaseModel, ValidationError
app = FastAPI()
class Item(BaseModel):
name: str
tags: List[str]
@app.post(
"/items/",
openapi_extra={
"requestBody": {
"content": {"application/x-yaml": {"schema": Item.schema()}},
"required": True,
},
},
)
async def create_item(request: Request):
raw_body = await request.body()
try:
data = yaml.safe_load(raw_body)
except yaml.YAMLError:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail="Invalid YAML")
try:
item = Item.parse_obj(data)
except ValidationError as e:
raise HTTPException(status_code=422, detail=e.errors())
return item
信息
在Pydantic版本1中,解析和验证对象的方法是Item.parse_obj(),在Pydantic版本2中,该方法称为Item.model_validate()。
提示
在这里,我们重用了相同的Pydantic模型。
但同样地,我们也可以用其他方式进行验证。